Introduction
For more than 6,000 years, foenegriek (fenugreek )(Trigonella foenum-graecum) has been valued as both a kitchen staple and a trusted herbal remedy. Known in India as methi seeds, this ancient legume bridges traditional wisdom and modern science, offering benefits that range from blood sugar control to heart health.
A Rich History Across Continents
Fenugreek’s origins lie in the Mediterranean and Central Asia. Archaeologists have found seeds from 4000 BC in Iraq, and ancient physicians from Punjab to Persia praised its healing power.
Today, fenugreek is cultivated in India, Pakistan, Afghanistan, Iran, Egypt, France, Spain, Turkey, Morocco, and beyond. Its resilience in semi-arid climates has ensured its place in global agriculture.
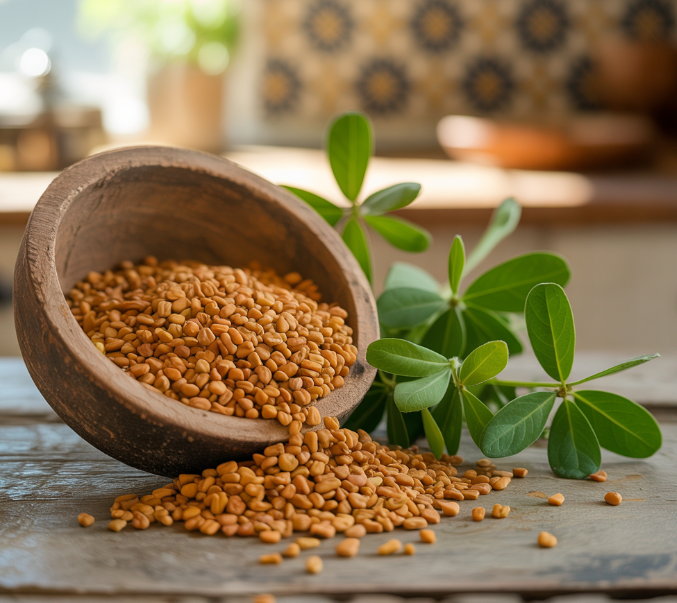

Nutritional Value
: Key Nutrients in Fenugreek Seeds
-
Carbohydrates: ~60%
-
Dietary Fiber: ~25%
-
Protein: ~23g per 100g
-
Healthy Fats: Oleic and linolenic acids
-
Minerals: Potassium, magnesium, calcium, iron, manganese, zinc
-
Vitamins: A, B1, B2, C, niacin
Nutrition Snapshot (per tablespoon/11g):
-
Calories: 35
-
Fiber: 3g
-
Protein: 3g
-
Iron: 21% DV
(Image Alt Text: Close-up of fenugreek seeds in a wooden bowl with a measuring spoon)
Health Benefits of Fenugreek
1. Blood Sugar Control
Fenugreek’s soluble fiber and plant compounds help lower fasting glucose levels and improve insulin sensitivity, making it a natural choice for type 2 diabetes prevention.
2. Heart Health Support
By reducing LDL cholesterol and improving lipid metabolism, fenugreek supports long-term cardiovascular wellness.
3. Women’s Wellness
Fenugreek acts as a natural lactation booster, eases menstrual cramps, balances hormones in PCOS, and reduces menopausal symptoms.
4. Exercise Performance
Athletes use fenugreek extracts for testosterone support and muscle development.
5. Other Benefits
With anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-carcinogenic properties, fenugreek has earned its place in herbal medicine.
Traditional Uses in Food and Medicine
Culinary Uses:
-
Roasted seeds in curries, spice blends, and pickles
-
Fresh leaves in vegetable dishes
-
Fenugreek tea for digestion and wellness
Medicinal Uses:
-
Digestive aid and natural laxative
-
Remedy for respiratory issues and fever
-
Strengthening tonic in Ayurveda
(Image Alt Text: Fenugreek tea in a glass cup with seeds scattered on the table)
Side Effects and Precautions
-
May cause bloating, gas, or diarrhea
-
Can trigger allergies in those sensitive to legumes
-
May produce a maple syrup-like odor in sweat/urine
-
Avoid high doses during pregnancy (possible early contractions)
-
Discontinue two weeks before surgery (slows blood clotting)
Recommended Dosages
-
Diabetes/Cholesterol: 5–25g seeds daily
-
Testosterone Support: 250–600mg extract
-
Lactation: 1–6g seeds daily
(Always consult a healthcare provider before starting supplementation)
Final Thoughts
From ancient herbal traditions to modern health research, fenugreek remains a powerful yet accessible superfood. Whether sprinkled in food, brewed as tea, or taken as a supplement, it offers science-backed benefits for blood sugar balance, heart health, women’s wellness, and more.
As Avicenna wisely said:
“Fenugreek is the first stop to curing winter chills.”
In short, the best remedies may be the ones our ancestors trusted all along.
✅ Pro Tip for Readers: Start small — add a pinch of fenugreek powder to soups or try fenugreek tea daily to enjoy its benefits naturally.